10 Rules from Seth Klarman
Seth Klarman is one of the best investors in the world.
He returned over 20% for more than 40 years.
His book Margin of Safety sells for over $1,700 on Amazon. Let’s share 10 key investment lessons today.
Who is Seth Klarman?
Seth Klarman is a legendary value investor.
He is known as “The Oracle of Boston” and is highly respected in the investment world.
Klarman was born in 1957 in New York City, and used to spend a lot of time reading baseball statistics in the newspaper.
The next section in the newspaper was the Finance & Investing section.
That made Klarman getting interested in investing, and at the age of 10, he bought his first stock: Johnson & Johnson (J&J).
Seth Klarman was no ordinary student.
After graduating from Cornell, he earned his MBA from Harvard Business School, where his sharp mind quickly stood out.
As he was finishing his degree at age 25, a group of his professors approached him with an unusual offer:
They wanted Seth to help them invest and manage their money.
Klarman weighed the choice carefully. He had offers from top Wall Street firms that came with huge paychecks, but he was more interested in building something meaningful.
So in 1982, he said yes to his professors.
That year, Klarman and four Harvard professors founded The Baupost Group, a firm built on the timeless principles of value investing.
Over 40 years, Baupost Group grew to one of the largest hedge funds in the world.
They manage over $24 billion today and achieved an average annual return of over 20%.
Seth Klarman has been the CEO since the beginning and made himself a fortune of $1.3 billion.
He explained all his secrets in his book ‘Margin of Safety’.
Copies of the book are very limited, they sell for $1,000 or more on Amazon today.
One of the reasons he’s so successful? He is willing to make bold bets.
Sometimes, Seth Klarman sits on 30-50% cash, waiting for the right timing to swing heavily.
Someone who looks up to Klarman’s excellent risk management? Warren Buffett.
Margin of Safety
His book Margin of Safety was published in 1991.
At that time, the stock market was booming. Wall Street was selling IPOs, bonds, and complex new products like crazy.
Investors were chasing quick profits and ignoring risk.
They were acting like speculators, and not intelligent investors.
Klarman wrote Margin of Safety to remind people about the core principles of value investing and the importance of protecting your money.
But nobody wanted to listen when making big profits seemed so easy.
The book was a commercial flop, and quickly went out of print.
Klarman even gave away copies for free.
Then came the dot-com crash and the 2008 financial crisis.
Stocks collapsed, speculators lost everything, and only disciplined value investors, like Klarman, held up.
That’s when things changed: everyone wanted to learn from him.
Margin of Safety became one of the most sought-after investing books ever written.
Klarman never reprinted it. He preferred it to stay rare and low-profile.
That’s why today, original copies sell for over $1,000 online.
10 Lessons from Margin of Safety
At Compounding Quality we had the privilege to read the book.
Here are 10 interesting lessons from Margin of Safety:
1. Speculators versus Investors
Klarman says there are two kinds of people in the market:
Speculators: They buy stocks, crypto, or NFTs based on market hype and hope the prices go up to quickly make a profit
Investors: They think like owners when buying a stock. They look at it as a business, understanding what it does, how much value it creates, and how much it is worth based on that
In short: Speculators bet on prices, investors bet on businesses.
2. Always use a Margin of Safety
Imagine you bought a stock whose intrinsic value is $100 but is trading at $60.
That $40 is your margin of safety.
The larger the margin of safety, the less risk you’re taking.
“You don’t reduce risk by buying “safer” companies. You reduce risk by paying a ‘safer’ price.” - Seth Klarman3. Never Lose Money
There are 2 important rules in investing.
Rule #1: Do not lose money.
Rule #2: Do not forget Rule #1.
It is more important to avoid a big loss than to get a big win.
4. Use Mr. Market to your advantage
Klarman says the market has two moods:
Some days, the market thinks everything will be amazing: prices shoot up.
Other days, it thinks everything is falling apart: prices drop fast.
In other words: Mr. Market is a Manic-Depressive.
As investors, we can’t get caught up in either mood.
Don’t overpay when everyone’s excited. Don’t freeze when everyone’s scared.
Stay calm, be patient, and act only when the price is right.
5. Don’t Follow the Crowd
It’s easy to get excited about a ‘hot stock’.
Seth Klarman warns that by the time a stock becomes popular, it’s usually no longer cheap.
Real value investors don’t chase what everyone else is buying.
They look for strong, overlooked businesses that the market hasn’t noticed yet.
That’s where the real opportunity lies.
“You must buy on the way down. There is far more volume on the way down than on the way back up, and far less competition among buyers. It is almost always better to be too early than too late, but you must be prepared for price markdowns on what you buy.” - Seth Klarman6. The intrinsic value of a company
Analysts try to determine the intrinsic value of a company to two decimal spaces.
Seth Klarman absolutely hates this.
He says that every company contains risks. You can never value it to an exact number.
The more important question is:
"The big question is not whether a company is worth $100 or $105. It's whether a company is worth $100 or $200."Your job as an investor is to buy the company at a lower price using a margin of safety.
Let’s look at an example.
Imagine a company that’s growing and expected to earn more money over time.
You believe in its future.
Now, estimate what the stock is worth under different scenarios
What if things go well?
What if sales slow down?
Let’s say your fair value range is $60–$80 per share.
To protect yourself, you only buy the company at a stock price below $50.
This provides you with a margin of safety.
7. How to select stocks
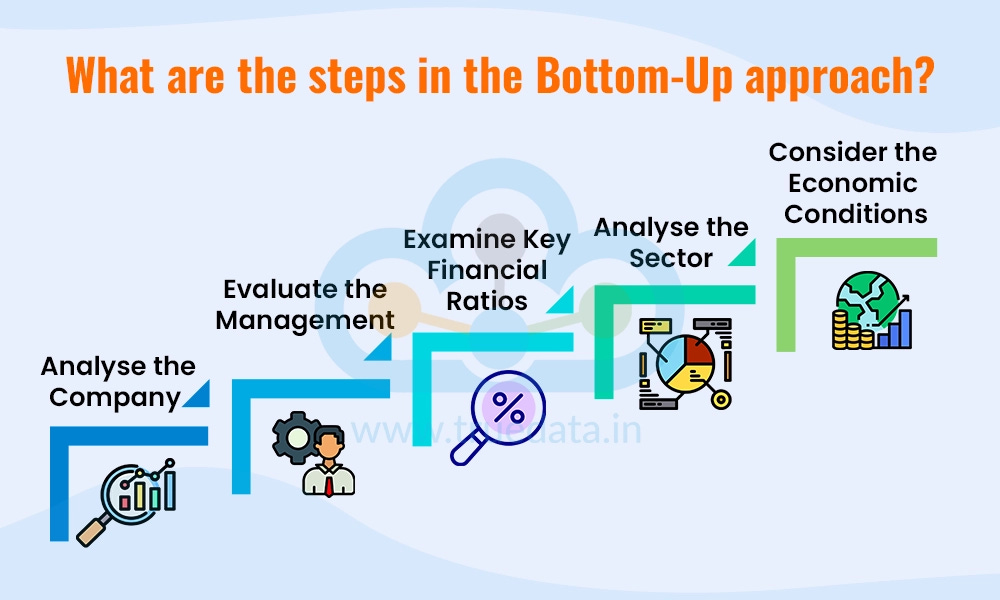
There are two approaches to select stocks:
Top-down approach: Looking at the (macro)economy to base your investments on.
Bottom-up approach: Looking at individual companies and buy wonderful companies at a fair price.
The best approach? Be a bottom-up stock picker.
8. Find the “Catalyst”
What is a Catalyst?
A catalyst is an event that forces the market to “wake up” and see the true value of a company. Do you think all undervalued stocks outperform the market?
This isn’t the case.
Undervalued companies can remain undervalued for years.
They need a catalyst to make the market recognize their undervaluation.
What could be a catalyst?
A new CEO is coming in to turn things around
The company is planning to sell off a bad division
The company is about to do a huge share buyback
These events attract market attention, which drives the stock price up.
9. Wall Street is Not Your Friend
Wall Street is a sales machine, making its money via fees.
Your broker wants you to trade as much as possible. This makes them their commission
Your bank wants you to buy new products. They do not care if you lose money
Investing success comes from understanding companies, buying when the time is right, and being patient enough to let compounding work in your favor.
Not from listening to Wall Street or trading frequently.
Successful investing = Research + Confidence + Patience + Margin of Safety 10. Patience is Your Superpower
Most investors want to make a quick profit.
But, money always flows from the impatient to the patient investors.
You need to wait for the right time to buy a stock at the right price, then hold on.
Conclusion
That’s it for today.
Here’s what you should remember from today’s article:
Seth Klarman generated a return of +20% per year for over 40 years
His book Margin of Safety teaches you to focus on risk management first and always use a Margin of Safety
He often holds lots of cash so he can strike when markets panic and prices get cheap.
Never invest in hypes
His investment philosophy in 3 steps:
Stay calm
Be patient
Buy great businesses
Everything in life compounds
Pieter (Compounding Quality)
PS You are not a Partner of Compounding Quality yet? Discover everything you need to know here.
Book
Order your copy of The Art of Quality Investing here
Used sources
Interactive Brokers: Portfolio data and executing all transactions
Fiscal: Financial data












Seth Klarman's book is a joy to read! Physical copies are indeed very expensive. PDF copies can be found online. Google is your friend. 🙂